Advancing Sandblasting and Coating Solutions with SR&ED Tax Credits
Sandblasting and coating solutions companies often face complex challenges as they work to enhance material adhesion, durability, corrosion resistance, and environmental sustainability. The Scientific Research and Experimental Development (SR&ED) tax credit program is an invaluable resource for these companies. It enables them to secure support for projects involving technological uncertainties and innovation. Here’s a look at some SR&ED-eligible activities in the sandblasting and coating solutions industry.
-
Developing Innovative Coating Materials
Challenge: Modernizing coatings with enhanced adhesion, durability, and resistance to environmental stressors.
Technological Uncertainty: Formulating a coating that strikes the right balance between strength and flexibility often requires substantial experimentation with materials and mixtures.
SR&ED Example: Developing a new, corrosion-resistant coating might require testing a variety of chemical additives, binders, and resins to optimize the application process. Testing would involve systematic adjustments to address how well the coating adheres, its weathering properties, and its longevity on diverse surfaces.
-
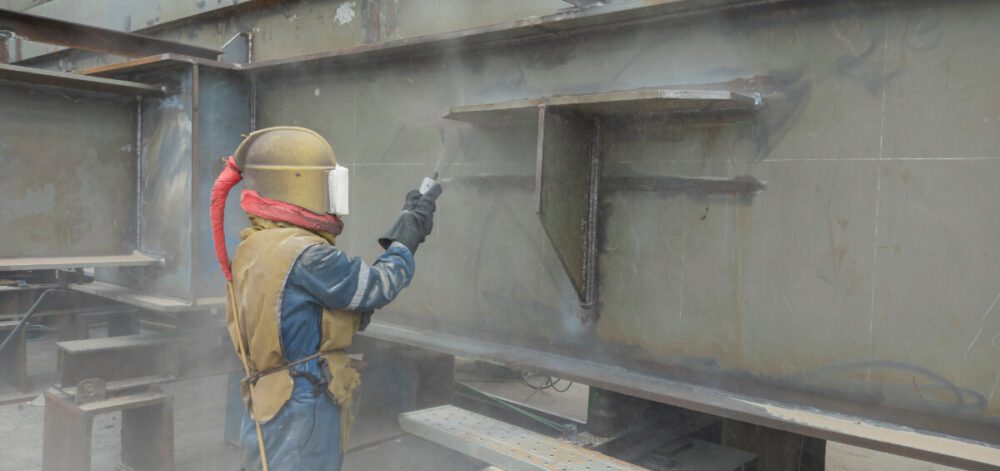
Enhancing Sandblasting Techniques for Efficiency
Challenge: Improving sandblasting techniques to deliver consistent, high-quality surface preparation with minimal waste and maximum efficiency.
Technological Uncertainty: Determining the most effective abrasive materials, nozzle designs, and pressure levels for different substrates introduces challenges. This is especially true as each surface reacts differently.
SR&ED Example: A company might experiment with various abrasive materials (e.g., glass beads, aluminum oxide) and nozzles to achieve optimal cleaning on metal surfaces without causing etching or damage. Documenting the testing process and results provides critical data for the SR&ED claim.
-
Integrating Automation and Robotics in Coating Application
Challenge: Implementing robotics for precise coating application on products with varying shapes and sizes.
Technological Uncertainty: Designing robots that adapt to different geometries, ensuring consistent coating thickness and quality, poses significant technical challenges.
SR&ED Example: Engineers may develop and refine robotic programming and sensors to control coating thickness and coverage on irregular surfaces. Through iterative testing and reprogramming, the team works to optimize the robot’s adaptability. This will ultimately create a viable solution that improves consistency and reduces waste.
-
Creating Environmentally Friendly Coating Solutions
Challenge: Developing coatings that are eco-friendly while still meeting performance standards and compliance regulations.
Technological Uncertainty: Finding substitutes for potentially harmful materials and integrating them without losing product durability requires innovation and testing.
SR&ED Example: To create a non-toxic coating with comparable adhesion properties, a team may experiment with bio-based additives and alternative solvents. The process requires a balance between environmental safety and functional resilience. This occurs as teams test various compositions for effectiveness in different environments.
-
Advanced Monitoring and Quality Control Systems: Sandblasting and Coating
Challenge: Implementing real-time monitoring systems to ensure coatings meet quality standards throughout the application process.
Technological Uncertainty: Developing and implementing sensors capable of detecting defects, inconsistencies, or adherence issues is an ongoing R&D challenge.
SR&ED Example: A company might prototype a digital quality control system that captures and analyzes coating data in real-time, refining algorithms to detect irregularities in the application process. This iterative refinement requires both software and hardware advancements, providing essential insights for the SR&ED claim.
-
Innovating Corrosion Prevention in Harsh Environments
Challenge: Designing coatings that can withstand corrosion in demanding environments like marine or industrial settings.
Technological Uncertainty: Determining the optimal material mix for these coatings while maintaining resistance to moisture, salt, and other environmental factors is a core
challenge.
SR&ED Example: Research may focus on selecting and combining materials to create a corrosion-resistant coating, testing and refining these mixes to observe how each formulation resists specific environmental stressors. This extensive testing qualifies as SR&ED, as it involves experimental development and significant technical uncertainty.
-
Energy-Efficient Sandblasting Equipment
Challenge: Reducing the energy footprint of sandblasting equipment without compromising on effectiveness.
Technological Uncertainty: Achieving the desired energy efficiency often requires testing various design changes, materials, and technologies.
SR&ED Example: Engineers might conduct a series of design iterations on sandblasting equipment to reduce energy consumption, experimenting with novel materials, nozzle configurations, and air compression techniques. By documenting each iteration, they develop a process that maximizes efficiency, supporting the case for SR&ED eligibility.
Maximize Your SR&ED Claim with Expert Guidance
For companies in sandblasting and coating solutions, navigating the SR&ED claim process can be complex but rewarding. Ayming Canada’s experienced SR&ED consultants can help identify and document eligible projects, ensuring your innovations receive the maximum possible tax credit.
Are you innovating in sandblasting or coating solutions? Connect with Ayming Canada to learn how we can help you unlock the potential of SR&ED tax credits and continue driving advancements in surface treatment technology.
Contact us today!
One of our experts will be in touch shortly.












No Comments